902 Specialist Orthopaedic Education
Back Pain

What is back pain?
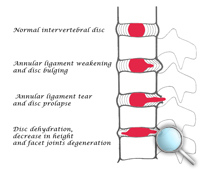
1. Degeneration
The rate of degneration varies from people to people. Generally, the interverbral discs and joints become unstable after aged 30. These changes may lead to back pain or sciatia caused by nerve compression.
2. Bone Projection / Over-growth
Osteophytes (bone spur) form naturally in the spine as a person ages and are normal reaction to degeneration. In most cases, the spurs are not the source of back pain. However, if the bone projections compress the adjunct nerves and suppress the blood supply to the nerve, the patients would suffer from leg pain during standing or walking.
3. Others
If the back pain is caused by tumor/ cancer or bacterial infections, patients may experience persistent and exacerbating pain in back, leading to night pain and other associated syndromes.
Back Pain - prevention
Exercise is an effective way to strengthen your muscles. The strong muscles can help to maintain a correct position of the spine. Low-impact activities can increase overall fitness without straining the back.
Back Pain – treatment and surgeries
1. Physiotherapy. It can be classified as active and passive treatments.
Active – effectively strengthen the patient’s muscles through persistent specific exercise.
Passive – relieve pain by various modalities including specific forms of electric current.
Misconceptions:
Many patients believe that reduction of physical activities can relieve their pain conditions, However, prolonged abstinence from normal activities may lead to chronic pain. Staying active is beneficial for pain relief. You are recommend to consult physiotherapist to personalize an exercise plan for you.
2. Medication
Depends on the severity of pain, orthopaedic doctors would prescribe oral medications for pain relief. If needed and appropriate, orthopaedic doctors may recommend intramuscular or nerve block to control your back pain.
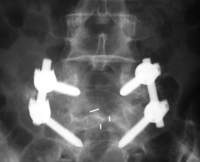
3. Surgery
Orthopaedic doctors would recommend surgery if needed, especially for conditions:
- Medications and physiotherapy fail to control the severe pain.
- Incontinence caused by severe nerve compression.
- Progressive muscle weakness caused by nerve compression.
- No improvement of pain conditions after 4-6 weeks of medication and physiotherapy treatment.
The information provided on this website are for educational purposes only. Please consult your physicians before considering treatment or for detailed medical advice.




